What is Pubalgia?
Pubalgia is defined as pain in the groin and pubic region. This pain may radiate to the medial thigh area (adductors) and/or to the lower abdomen.
The pain could come from a pathology in the tendons of the muscles that insert into the pubis, nerve entrapments, presence of a possible inguinal hernia and/or an inflammation of the pubic bone. The onset of pain is usually gradual and gets progressively worse over time, therefore, it would be recommended to see a health professional before the symptoms worsen.
It is a very common injury in runners and soccer players, due to the stress of repetitive movements on the pubis.
Causes of pubalgia
- Muscle imbalances of the hip and/or abdominal muscles.
- Muscular overloads of the adductor muscles.
- Problems in the transverse fascia of the abdominal wall.
- Chronic stress on the pubic joint.
Diagnosis of pubalgia
In cases of pubalgia, an anamnesis, a physical examination and an ultrasound should be performed in order to establish the degree of injury and make a prognosis and appropriate treatment plan. In this injury, it is very important to perform a correct exploration to be able to determine which is the pathology that is causing the pain. The diagnosis could be complemented with an MRI to obtain more detailed data of the injury.
Symptoms of pubalgia
The main symptoms are:
- Pain in the pubis and/or peripheral areas.
- Pain that increases with activity and improves with rest, although in very acute stages there may be pain even at rest.
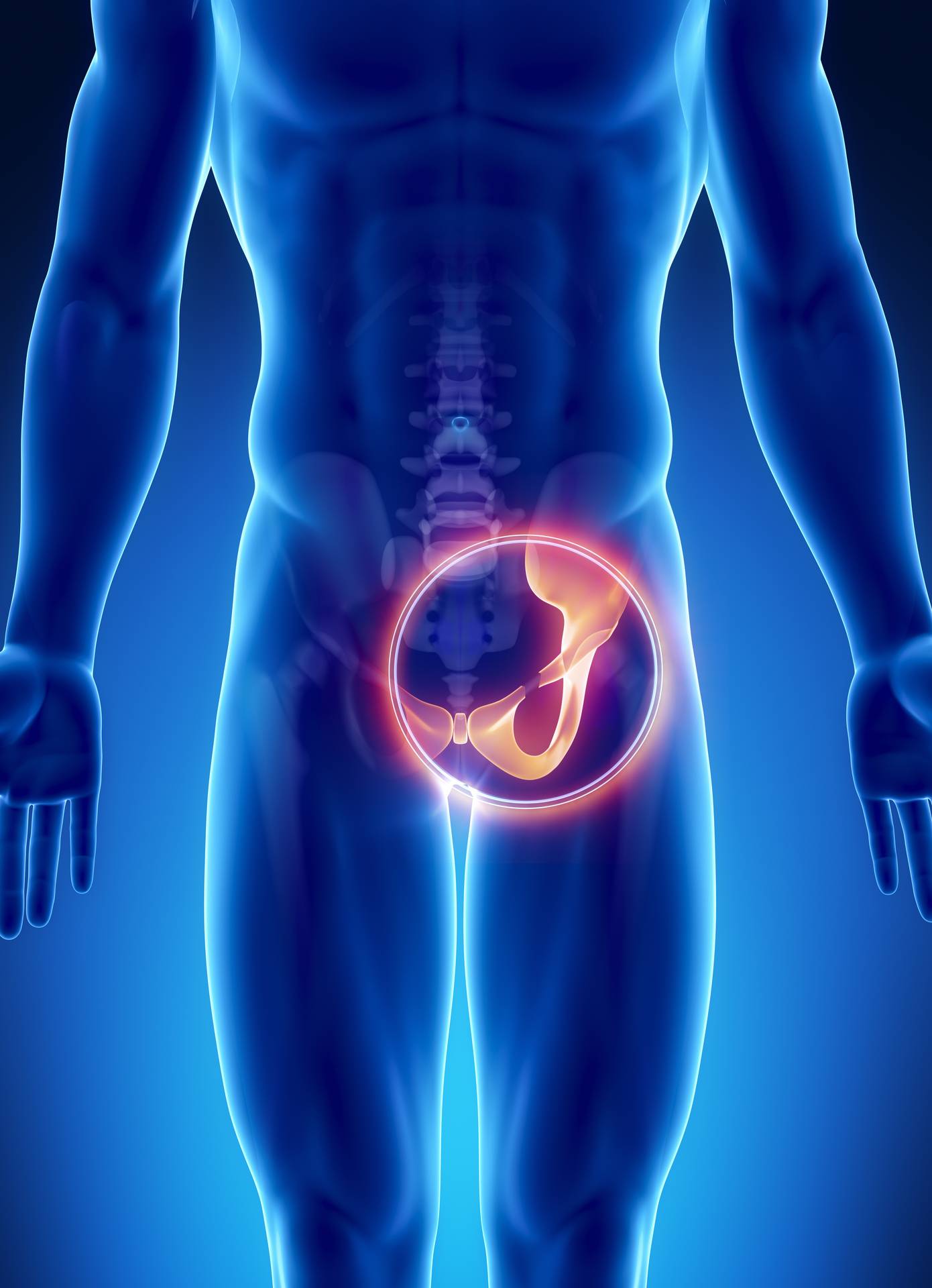
Treatment for pubalgia
In the first (acute) phase, where pain predominates, rest and anti-inflammatory therapies are recommended to relieve it. After this first phase, we will begin to work on the cause of the pain. The therapies used during treatment are:
- Manual therapy
- Cryotherapy
- Radiofrequency
- Percutaneous Intratisular Electrolysis (PIE)
- Dry needling
- Shock waves
- Neuromodulation
- Therapeutic exercise
- Osteopathy
- Electrostimulation
In this injury, it should be taken into account that its best treatment is to carry out adequate prevention and see a physiotherapist at the onset of symptoms.
Recovery from Pubalgia
Recovery will depend on the degree of the injury, the cause of the pain and the individual regenerative capacity of each person. This will cause the injury to recover in one month or it may take up to 10 months. The most frequent statistically is an average of 2 or 3 months to return to the level of activity before the injury.
PUBALGIA. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What does the body’s regenerative capacity depend on?
The healing of an injury or physical pathology is the responsibility of our body, in it there are some automatic mechanisms that are activated when we lose the normal physical or organic balance. These mechanisms are complex and depend largely on metabolism (biochemical, hormonal and neuronal processes). If these mechanisms work at 100%, we will be protected from a large number of impacts that our body may suffer at different levels (physical, emotional, biochemical and energetic) but if these mechanisms are diminished in their function, the ability of recovery and regeneration of our cells will be compromised, and may block the healing processes to an illness or injury temporarily or permanently. This will be very important to take into account when treating any injury or pathology, otherwise the patient will be able to perform multiple physical treatments on an injury without obtaining results.
How is the treatment planning?
The planning of this type of therapy is always personalized, giving priority in the early stages of treatment to reduce pain, inflammation and improve the mechanical and metabolic factors that have caused the injury. If we have to focus on the latter (because there is evidence of a deficit of function in the patient’s tissue regeneration mechanisms) then we will first set a guideline for the patient to perform at home for 3-6 weeks consistently:
Improved dietary hygiene
Natural supplementation: Detoxifying-anti-inflammatory-regenerating.
Exercises-stretching
Subsequently, we will begin with the Advanced Physiotherapy and Functional Training plan.
Should I suspend professional or sporting activity?
It will depend on each case and the degree of involvement of the injury.
How many sessions do I need to start noticing improvement?
It depends on each case, but normally with the use of state-of-the-art therapies such as those applied in Corporis the improvement is felt from the first session.
What is an ankle sprain?
An ankle sprain is one of the most common lower limb injuries treated in the clinic. It is the injury of the ligaments that support the ankle joint in a sudden movement of the foot outward or inward, thus causing an injury due to overstretching of this structure.
Share
related posts
This post is also available in: Spanish
Follow Us
Contact
LAST POSTS
 WE COLLABORATED IN THE SOLIDARITY PADEL TOURNAMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF THE CESARE SCARIOLO FOUNDATION -
WE COLLABORATED IN THE SOLIDARITY PADEL TOURNAMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF THE CESARE SCARIOLO FOUNDATION -  New Health Packs Corporis Christmas -
New Health Packs Corporis Christmas -  THIS MONTH, UP TO €50 DISCOUNT ON PHYSIOTHERAPY VOUCHERS -
THIS MONTH, UP TO €50 DISCOUNT ON PHYSIOTHERAPY VOUCHERS -  OSTEOARTHRITIS AND PHYSIOTHERAPY: THE ROLE OF PHYSIOTHERAPY IN THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF PEOPLE AFFECTED -
OSTEOARTHRITIS AND PHYSIOTHERAPY: THE ROLE OF PHYSIOTHERAPY IN THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF PEOPLE AFFECTED -
Working Hours
PHONE SERVICE (M-F)
09:00 – 20:00 hrs
CLINICAL CARE
Monday – Thursday
08:00 – 21:00 hrs
Friday
08:00 – 15:00 hrs
Therapeutic care by appointment.